VPN servers and VPN clients both play crucial roles in establishing secure connections over the internet. Understanding their differences is essential for setting up a reliable virtual private network.
A VPN server is the central hub of a VPN network. It manages connections and routes data securely. On the other hand, a VPN client is software or a device that connects to the VPN server. It initiates the connection and ensures data travels securely to and from the server.
Knowing the functions of both can help you choose the right VPN setup for your needs. In this blog post, we will explore the key differences between a VPN server and a VPN client, shedding light on their roles and how they work together to provide secure internet access.
VPN Basics
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) helps protect your online privacy. It creates a secure connection between your device and the internet. This section will explain the basics of VPNs.
What Is A VPN?
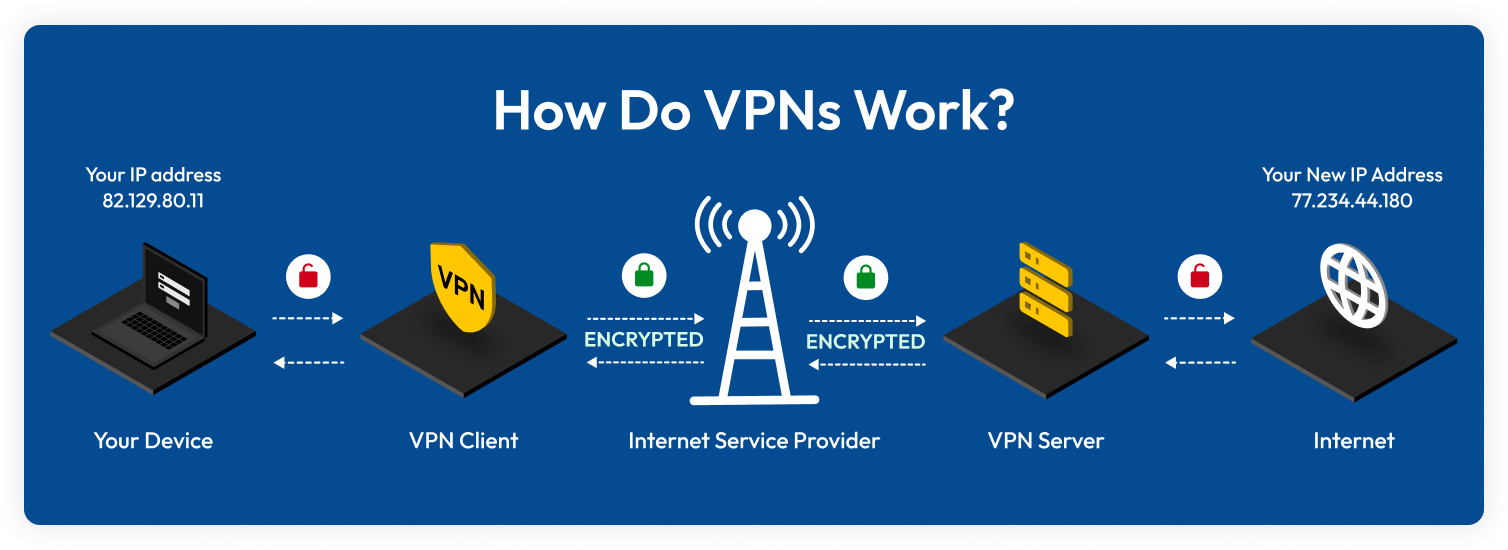
A VPN is a service that encrypts your internet connection. It hides your IP address and secures your data. This makes it harder for others to track your online activity. VPNs are useful for protecting sensitive information, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
How VPNs Work
VPNs work by creating a secure tunnel between your device and a VPN server. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- You connect to the internet through your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
- You then connect to a VPN server using VPN software.
- The VPN server encrypts your data and hides your IP address.
- Your data is then sent to its destination, such as a website or online service.
This process helps keep your online activity private and secure.
VPN Server
A VPN Server is a crucial component of a Virtual Private Network. It provides secure and encrypted connections. This allows users to access resources remotely and safely.
Definition Of VPN Server
A VPN Server is a dedicated server that manages VPN connections. It encrypts data and forwards it between the user’s device and the internet. This ensures privacy and security.
The VPN Server masks the user’s IP address. This makes it look like the user is browsing from the server’s location. It helps in bypassing geographical restrictions and ensures anonymity.
Functions Of A VPN Server
VPN Servers have several functions:
- Data Encryption: They encrypt data to protect it from hackers.
- IP Masking: They hide the user’s real IP address.
- Secure Remote Access: They allow secure access to resources remotely.
- Bypass Restrictions: They help in accessing geo-blocked content.
VPN Servers are also responsible for authenticating users. They ensure that only authorized users can access the network. This adds an extra layer of security.
Overall, a VPN Server is essential for maintaining privacy and security online. It provides a secure gateway for internet access. This makes it a vital tool for both individuals and businesses.
VPN Client
A VPN client is a software application that allows users to connect to a VPN server. It creates a secure connection, ensuring privacy and data protection. It acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. Understanding a VPN client is key to using VPN services effectively.
Definition Of VPN Client
A VPN client is a program installed on your device. It initiates the connection to a VPN server. Once connected, it encrypts your internet traffic. This makes your online activities private and secure. The VPN client also assigns you a new IP address. This masks your actual location.
Functions Of A VPN Client
The primary function of a VPN client is to establish a secure link. It connects to a VPN server through an encrypted tunnel. Here are some key functions:
- Data Encryption: It encrypts your internet traffic, keeping it secure from hackers.
- IP Masking: It hides your real IP address, giving you a new one.
- Access Control: It ensures that only authorized users can connect to the VPN.
- Bypassing Geo-restrictions: It allows access to content restricted by location.
VPN clients are essential for maintaining online privacy. They provide a secure browsing experience. Users can surf the web without fear of data theft. VPN clients also help in accessing region-locked content.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Encrypts data to prevent unauthorized access. |
| IP Masking | Changes your IP address to hide your location. |
| Access Control | Limits VPN access to authorized users. |
| Bypassing Geo-restrictions | Allows access to geographically restricted content. |
In conclusion, a VPN client is a vital tool for secure internet use. It offers many functions to protect your privacy. Installing a VPN client can enhance your online security.

Credit: symlexvpn.com
Key Differences
Understanding the key differences between a VPN server and a VPN client is crucial. These roles are distinct, serving different purposes in the VPN ecosystem. Let’s delve deeper into the specific roles and data handling differences between VPN servers and VPN clients.
Server Vs Client Role
The VPN server acts as the core of the VPN network. It manages and directs all incoming and outgoing traffic. The server’s main role is to provide secure connections to multiple clients.
On the other hand, the VPN client is the user-end application or device. It connects to the VPN server to access the network securely. The client’s main role is to initiate a secure connection to the server.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Aspect | VPN Server | VPN Client |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Manages network | Connects to network |
| Control | High | Low |
| Setup | Complex | Simple |
Data Handling Differences
The VPN server encrypts and decrypts data traffic for all clients. It ensures that the data is secure before it reaches its destination.
Conversely, the VPN client encrypts data before sending it to the server. Once the data reaches the server, it is decrypted and sent to the internet.
Important points to remember:
- Encryption: Both server and client encrypt data, but the server decrypts it.
- Data Flow: Data flows from client to server, then to the internet.
- Security: Both ends ensure data security through encryption.
Understanding these differences helps in setting up and using VPNs effectively. Both roles are essential for a secure and private internet experience.
Use Cases For VPN Servers
Understanding the use cases for VPN servers can help you see their importance. VPN servers are essential in various scenarios, particularly in business and security. Below, we explore how they are used in these areas.
Business Applications
VPN servers play a crucial role in business environments. They allow employees to access the company’s network securely from remote locations. This is especially useful for remote workers and traveling employees. With a VPN server, they can access internal resources, such as shared drives and intranet websites, without risking data breaches.
Another important use case is secure communication. Businesses can use VPN servers to encrypt communications between different offices. This ensures that sensitive information remains private and secure. Additionally, companies often use VPN servers to connect multiple office locations. This creates a unified network, making it easier to manage and share resources.
Here are some key benefits of using VPN servers in businesses:
- Remote access to internal resources
- Secure communication channels
- Improved data protection
- Cost-effective network management
Server Security
VPN servers are vital for server security. They act as a shield, protecting the server from unauthorized access. By using a VPN server, you can ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data. This is especially important for servers hosting critical information, such as financial records or customer data.
Another aspect of server security is data encryption. VPN servers encrypt data transmitted between the client and the server. This makes it difficult for hackers to intercept and read the data. Encryption adds an extra layer of security, making the server more robust against attacks.
Here are some key security features provided by VPN servers:
- Access control
- Data encryption
- Protection against DDoS attacks
- Improved anonymity
Using VPN servers is a smart choice for businesses and individuals who prioritize security and privacy. By implementing VPN servers, you can ensure your data remains safe and accessible only to authorized users.
Credit: www.keepersecurity.com
Use Cases For VPN Clients
VPN clients serve various purposes in today’s digital world. They are essential tools for individuals and organizations seeking secure and private internet access. Here are some common use cases for VPN clients:
Personal Privacy
Many people use VPN clients to protect their personal privacy online. With a VPN client, your internet traffic is encrypted, ensuring that no one can see what you are doing online. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi networks, where hackers can easily intercept data.
Additionally, a VPN client can mask your IP address. This prevents websites and online services from tracking your location and browsing habits. This level of anonymity is crucial for those who value their privacy.
Remote Access
VPN clients are also widely used for remote access. Employees can connect to their company’s network from anywhere in the world. This is particularly useful for remote workers and those who travel frequently. A VPN client creates a secure connection, allowing access to internal resources as if you were in the office.
Furthermore, businesses can ensure that data transmitted over the internet is secure. This reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. It also helps in maintaining compliance with data protection regulations.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Personal Privacy | Encrypts internet traffic and masks IP address. |
| Remote Access | Allows secure connection to a company’s network. |
In summary, VPN clients are crucial for personal privacy and remote access. They provide security, anonymity, and convenience for users worldwide.
Setup And Configuration
Understanding the setup and configuration of a VPN server and a VPN client is crucial for a seamless experience. The process involves different steps and requirements for each.
Setting Up A VPN Server
To set up a VPN server, you need to follow a series of steps:
- Choose a VPN server software: Options include OpenVPN, SoftEther, or WireGuard.
- Install the software: Download and install the chosen VPN server software on your server.
- Configure the server: Set up the necessary configurations, such as IP ranges, protocols, and encryption methods.
- Set up user authentication: Create user accounts and set passwords or other authentication methods.
- Open ports: Ensure that the necessary ports are open on your firewall or router.
- Test the connection: Verify that the VPN server is functioning correctly by connecting to it from a VPN client.
Installing A VPN Client
Installing a VPN client is generally simpler than setting up a server. Here are the steps:
- Select a VPN service: Choose a reliable VPN service provider that meets your needs.
- Download the client software: Obtain the VPN client software from the provider’s website or app store.
- Install the client: Follow the installation instructions specific to your operating system.
- Log in: Open the client software and log in using your credentials.
- Connect to a server: Select a VPN server from the list provided and connect.
- Verify the connection: Check that your IP address has changed and that your data is encrypted.
Choosing The Right VPN
Choosing the right VPN can be a daunting task. There are many factors to consider. Knowing the difference between a VPN server and a VPN client is essential. This knowledge helps you make an informed decision. Let’s explore the key factors and popular VPN providers.
Factors To Consider
- Security Protocols: Ensure the VPN uses strong security protocols like OpenVPN or IKEv2.
- Server Locations: Check if the VPN has servers in the locations you need.
- Speed: Look for a VPN with high-speed servers to avoid slow internet.
- Privacy Policy: Choose a VPN with a no-logs policy to protect your data.
- Compatibility: Ensure the VPN supports all your devices and operating systems.
- Customer Support: Opt for a VPN with 24/7 customer support.
Popular VPN Providers
| Provider | Key Features |
|---|---|
| NordVPN | Strong security, many server locations, fast speeds. |
| ExpressVPN | High-speed servers, strong encryption, user-friendly. |
| CyberGhost | Easy to use, good privacy policy, many servers. |
| Surfshark | Unlimited devices, strong security, affordable. |
| Private Internet Access | Strong privacy, many servers, good customer support. |
Choosing the right VPN is crucial for your online safety. Consider these factors and providers to make an informed choice. Whether you need it for privacy, speed, or security, the right VPN can make a big difference.
Credit: www.softether.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A VPN Server?
A VPN server is a remote server that provides VPN services. It encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure tunnel.
How Does A VPN Client Work?
A VPN client is software installed on your device. It connects to a VPN server and encrypts your internet traffic.
Why Use A VPN Server?
A VPN server enhances online privacy and security. It helps bypass geo-restrictions and access blocked content.
What Are The Benefits Of A VPN Client?
A VPN client protects your data on public Wi-Fi. It ensures anonymity and hides your IP address.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between a VPN server and a VPN client is crucial. A VPN server provides the service, while the client connects to it. This relationship enhances online privacy and security. Choosing the right VPN depends on your specific needs.
Remember, a VPN client is the user’s tool, and the server is the provider’s resource. Both play vital roles in ensuring safe internet use. Explore various options to find the best fit. Stay informed and protected online. Keep your data secure with the right VPN setup.