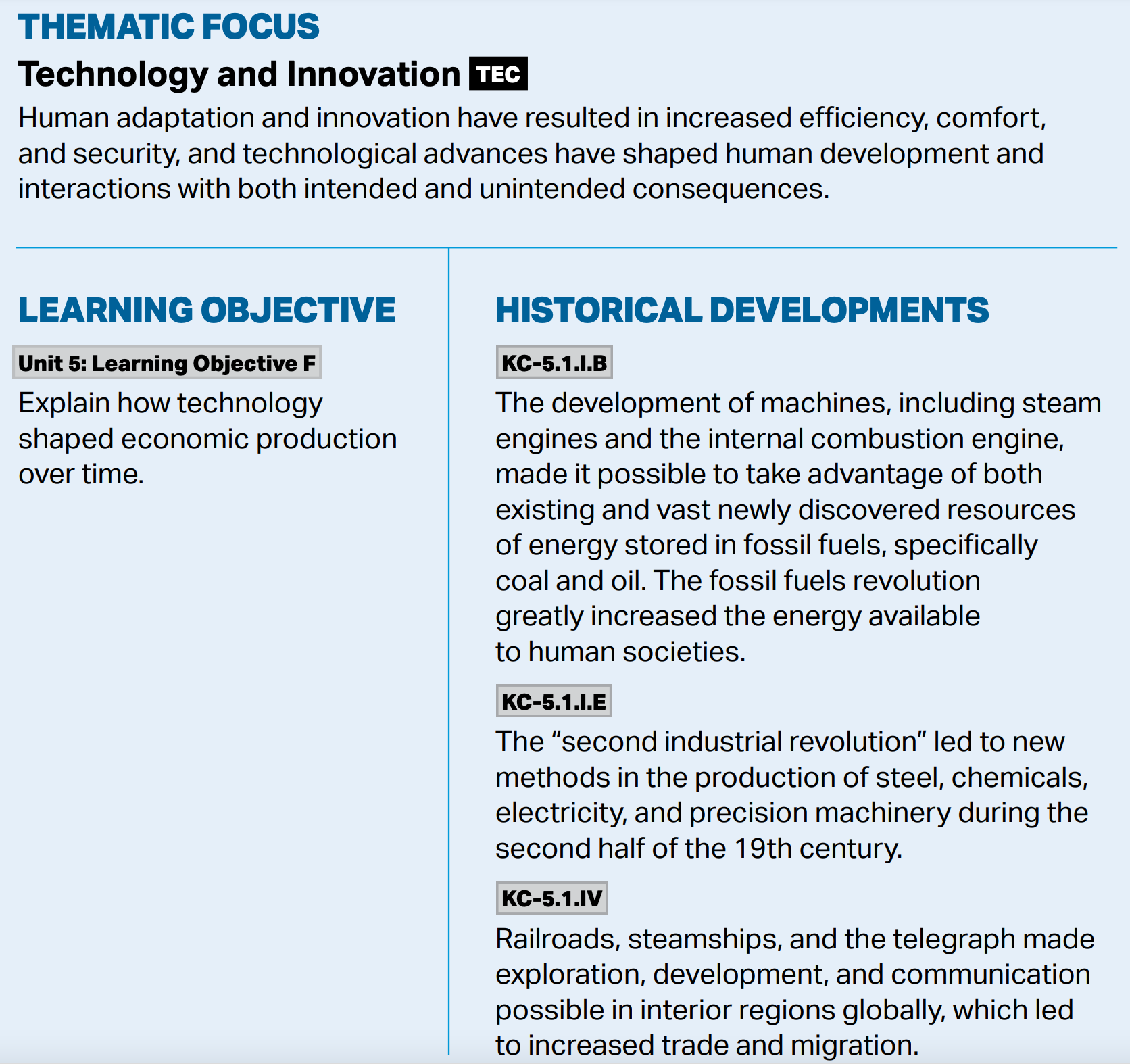
Technology has revolutionized economic production by automating tasks, increasing efficiency, enabling global trade, reducing costs, fostering innovation, transforming industries, and boosting economic growth.
The evolution of technology has continuously reshaped economies. In the early stages, machinery and steam engines revolutionized manufacturing. Later, electricity and assembly lines sped up production. The computer age introduced automation and data processing. Today, the internet and artificial intelligence drive innovation in every industry.
Each technological leap brought increased efficiency, lowered costs, and new opportunities. Understanding this progression helps us appreciate the current economic landscape. It also offers insights into future trends. This journey through technological advancements reveals a dynamic interplay between innovation and economic growth. Stay with us as we explore this fascinating topic in detail.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Early Technological Innovations
Technology has always played a crucial role in shaping economic production. From the earliest tools to modern-day machinery, technological innovations have continuously transformed how goods are produced and services are delivered. This evolution can be traced back to two significant periods: the Agricultural Revolution and the Industrial Revolution.
Agricultural Revolution
The Agricultural Revolution marked a pivotal shift from hunting and gathering to settled farming. This transition began around 10,000 BCE. Early humans learned to cultivate crops and domesticate animals. This led to a more stable food supply.
Key innovations included the plow and irrigation systems. The plow allowed farmers to till the soil more efficiently. This increased crop yields. Irrigation systems brought water to fields, ensuring crops could grow in dry areas. These advances reduced the labor needed for farming and supported larger populations.
The Agricultural Revolution also saw the development of crop rotation and selective breeding. Crop rotation helped maintain soil fertility. Selective breeding improved the quality of plants and animals. These practices boosted productivity and laid the foundation for future agricultural advancements.
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution began in the late 18th century. It marked a shift from manual labor to machine-based manufacturing. This period saw the rise of factories and mass production.
One of the key innovations was the steam engine. Invented by James Watt, it powered machinery and transportation. This innovation increased production speed and efficiency. Factories could now operate around the clock.
Another significant development was the spinning jenny. This machine revolutionized textile production. It allowed one worker to spin multiple spools of thread at once. This greatly increased output and reduced costs.
The Industrial Revolution also introduced the assembly line. Pioneered by Henry Ford, it transformed manufacturing. Each worker performed a specific task, speeding up production and lowering costs. This method became standard in many industries.
These early technological innovations laid the groundwork for modern economic production. They show how technology can drive progress and improve living standards.
Rise Of Industrial Machinery
The rise of industrial machinery marked a turning point in economic production. Machines started to replace human labor, increasing efficiency and output. This shift led to the Industrial Revolution, a period of rapid industrial growth. Factories grew, cities expanded, and the economy transformed.
Steam Power
Steam power played a crucial role in this transformation. James Watt improved the steam engine in the late 18th century. Factories used these engines to power machines, which greatly increased production speed.
Before steam power, industries relied on waterwheels and windmills. Steam engines freed factories from these limitations. They could be built anywhere, not just near water sources. This change allowed for more flexible and widespread industrial growth.
Steam engines also improved transportation. They powered trains and ships, which moved goods faster and cheaper. This improvement connected markets and boosted trade.
Mechanization Of Production
The mechanization of production involved using machines to perform tasks once done by hand. This change began in the textile industry with inventions like the spinning jenny and the power loom.
These machines spun thread and wove cloth much faster than people could. Factories began to produce large quantities of textiles at lower costs. This increase in production led to more affordable goods for consumers.
Mechanization spread to other industries. Agriculture saw the introduction of machines like the reaper and the plow. These tools made farming more efficient, leading to increased food production.
Overall, the mechanization of production boosted the economy. It created jobs, increased output, and lowered costs. This period set the stage for the modern industrial economy.
Technological Advancements In The 20th Century
Technological advancements in the 20th century transformed economic production. Factories became more efficient with automation and new machinery. Improved communication tools like the internet boosted global trade.
The 20th century brought rapid technological growth. This growth reshaped economic production. New inventions and innovations changed how industries operated. Two key areas of change were electrification and the automobile industry.
Electrification
Electrification transformed many industries. Factories could run machines longer and more efficiently. This led to increased production rates. Homes and businesses also benefited. Electric power brought new conveniences and improved quality of life.
Electricity powered new tools and machinery. This reduced manual labor. Workers could focus on more complex tasks. Communication also improved. The telephone and radio became widespread. These tools connected people and businesses like never before.
Automobile Industry
The automobile industry grew quickly in the 20th century. Cars became more affordable and common. This changed transportation and production. Factories adopted the assembly line. This method sped up production and lowered costs.
The rise of cars led to new jobs. Workers built roads, highways, and gas stations. The economy benefited from increased mobility. People could travel further for work and leisure. Businesses reached new markets and customers. This growth supported economic expansion.
Overall, technology in the 20th century had a huge impact. Electrification and the automobile industry are just two examples. These advancements shaped the economy and our daily lives.
“`
Information Age
The Information Age has transformed economic production in unimaginable ways. This era, starting in the late 20th century, saw technology advance at a rapid pace. It has affected how businesses operate and how economies grow.
Computing Technology
Computing technology has been a cornerstone of the Information Age. Computers have become faster, smaller, and more efficient over time. They have automated tasks that were once done manually. This has increased productivity and reduced costs for businesses. The development of software has further boosted efficiency. Programs can now handle complex calculations and data analysis quickly. This has allowed businesses to make better decisions based on data.
Internet Revolution
The internet revolution has been another major factor in economic production. It has connected people and businesses across the globe. This connectivity has opened up new markets and opportunities. E-commerce platforms have made it easier for businesses to reach customers. Online services have also streamlined operations. Companies can now collaborate in real-time, regardless of location. The internet has also facilitated the rise of digital goods and services. These have become significant contributors to economic growth.
Globalization And Technology
Globalization and Technology have reshaped economic production in significant ways. Technology has connected markets, enabling businesses to operate across borders more efficiently. This digital transformation has led to the rise of global supply chains, outsourcing, and offshoring.
Global Supply Chains
Technology has made global supply chains more efficient. Companies can now track products in real-time. This ensures timely deliveries and reduces costs. Here are some ways technology has improved supply chains:
- Real-time tracking: GPS and IoT devices offer precise tracking.
- Automation: Robots and AI handle tasks more efficiently.
- Data analytics: Predictive analytics help in demand forecasting.
- Blockchain: Ensures transparency and security in transactions.
Outsourcing And Offshoring
Technological advances have facilitated outsourcing and offshoring. Companies can now hire talent from around the world. This helps reduce costs and access skilled labor. Below are some benefits of outsourcing and offshoring:
- Cost savings: Labor costs are lower in some countries.
- Expertise: Access to specialized skills not available locally.
- Scalability: Businesses can scale operations quickly.
- Focus: Companies can focus on core activities.
In conclusion, technology has been a key driver in globalization. It has enabled businesses to operate more efficiently and on a global scale.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies have significantly impacted economic production. These advancements have reshaped industries, creating new opportunities and challenges. Understanding how these technologies influence economic production is crucial for businesses and individuals alike.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) has transformed many aspects of economic production. AI can analyze large amounts of data quickly. This helps businesses make informed decisions. AI-powered tools improve efficiency by automating complex tasks. Predictive analytics, a feature of AI, helps forecast market trends. This allows companies to plan better and reduce risks. AI also enhances customer service through chatbots and virtual assistants.
Automation And Robotics
Automation and robotics have revolutionized manufacturing and other industries. Automated systems increase production speed. They also reduce human error. Robotics handle repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for more complex roles. Automated warehouses streamline logistics and supply chain management. This reduces costs and improves delivery times. Robotics in healthcare assist in surgeries and patient care, improving outcomes and efficiency.
Economic Impacts
Technology has transformed economic production in many ways over the years. It has impacted how we produce goods, manage resources, and conduct business. This change has had significant economic impacts on productivity and employment.
Productivity Gains
Technological advancements have led to impressive productivity gains. Machines and software help workers complete tasks faster and more efficiently. Automation in factories has reduced the time needed to produce goods. Advanced software has streamlined business processes, saving time and money. These improvements have allowed businesses to produce more with less effort.
Job Displacement
While technology boosts productivity, it can also lead to job displacement. Automation and artificial intelligence have replaced many manual jobs. Some workers have found it hard to adapt to new technology. This shift has created a demand for new skills in the workforce. While some jobs disappear, new ones emerge in tech-driven industries. Workers often need retraining to stay relevant in the changing job market.
Credit: www.freeman-pedia.com
Future Trends
Technology has continuously reshaped how we produce goods and services. Future trends in technology promise even more profound changes. Let’s explore some of the most impactful trends.
Sustainable Technologies
Sustainable technologies are becoming essential. They help reduce environmental impact and ensure long-term economic growth. These technologies include renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. They also include energy-efficient machines and environmentally friendly production processes. Businesses are adopting these technologies to meet regulations and consumer demand for greener products.
Many companies now use recycled materials in their production processes. This practice reduces waste and conserves natural resources. For example, the fashion industry is using recycled fabrics to create new clothing lines. This trend is expected to grow as more industries recognize the benefits of sustainability.
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is changing how businesses operate. It involves integrating digital technologies into all areas of a business. This shift enhances efficiency, improves customer experiences, and opens new revenue streams.
One key aspect of digital transformation is the use of artificial intelligence (AI). AI helps businesses analyze data, predict trends, and automate tasks. For instance, AI can manage inventory, forecast demand, and even assist in customer service.
Another important element is the adoption of cloud computing. Cloud computing allows businesses to store and access data remotely. This technology provides flexibility, reduces costs, and enhances collaboration. Many businesses are moving their operations to the cloud to stay competitive.
The rise of e-commerce is also a significant part of digital transformation. Online shopping has become a major driver of economic production. Businesses are leveraging e-commerce platforms to reach a global audience. This trend is likely to continue as more consumers prefer online shopping.
| Technology | Impact |
|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Automation, data analysis, trend prediction |
| Cloud Computing | Data storage, cost reduction, collaboration |
| Renewable Energy | Environmental impact, cost savings |
In conclusion, technology will continue to shape economic production. Businesses need to embrace these trends to stay competitive and sustainable.

Credit: www.stuvia.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Has Technology Impacted Economic Production?
Technology has revolutionized economic production by automating processes, increasing efficiency, and reducing costs. Innovations like AI and robotics have streamlined manufacturing. Technology also enables better data analysis and faster decision-making. This ultimately boosts productivity and economic growth.
What Role Does Ai Play In Economic Production?
AI plays a crucial role in economic production by optimizing operations, predicting trends, and improving decision-making. It automates repetitive tasks, enhances precision, and reduces human error. AI-driven insights help businesses adapt quickly to market changes, thereby increasing efficiency and profitability.
How Has Automation Changed Manufacturing?
Automation has transformed manufacturing by increasing production speed, reducing labor costs, and enhancing product quality. Automated systems perform repetitive tasks with high precision and consistency. This leads to higher output and lower operational costs, making industries more competitive.
How Does Technology Influence Global Trade?
Technology influences global trade by improving communication, reducing shipping times, and enabling online transactions. Advanced logistics and tracking systems streamline supply chains. E-commerce platforms facilitate international sales. This connectivity boosts trade efficiency and expands market reach.
Conclusion
Technology has transformed economic production throughout history. From the steam engine to the internet, advancements have driven efficiency. Businesses produce goods faster and cheaper now. Innovation continues to shape industries, enhancing productivity. As technology evolves, economic landscapes shift, creating new opportunities.
Embracing these changes is key for growth. By understanding technology’s impact, we can better navigate future economic trends. Stay informed and adaptable to thrive in this ever-changing environment.







