What is the Difference between Project Management And Operations Management: Key Insights
Project management focuses on temporary initiatives with specific goals, while operations management oversees ongoing processes to maintain efficiency and productivity in a business.
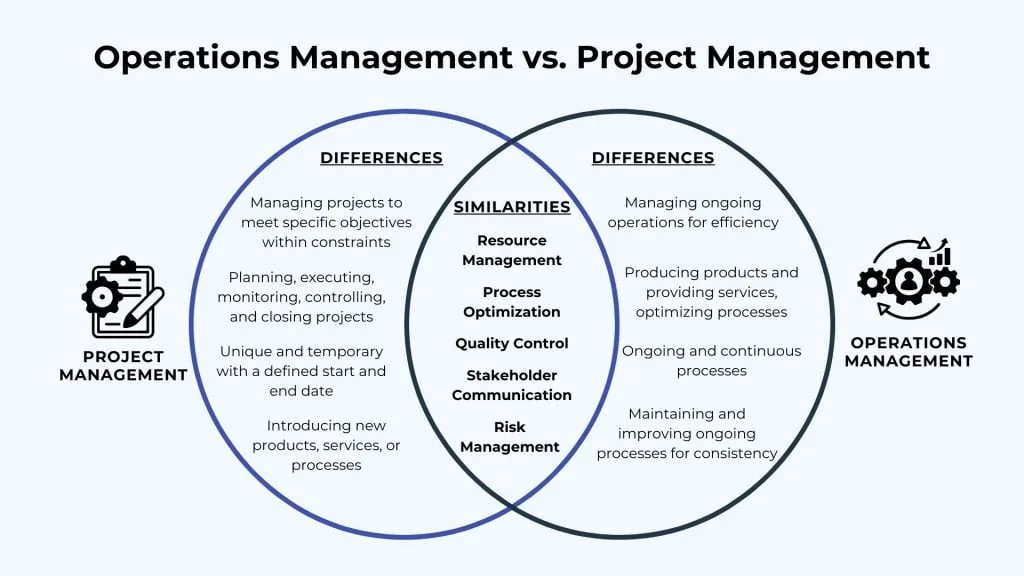
Understanding their differences is essential for effective management. Project management focuses on temporary endeavors, aiming to achieve specific goals within a set timeframe. Operations management, on the other hand, deals with ongoing processes, ensuring efficiency and consistency in daily activities.
Knowing these differences helps businesses allocate resources better and improve overall performance. This blog post will explore the key distinctions between project management and operations management, offering insights into their unique roles and benefits. Stay tuned to learn how each field contributes to organizational success and how understanding them can enhance your management skills.
Introduction To Management Disciplines
Management is a broad field. It includes various disciplines aimed at improving efficiency. Two key areas are Project Management and Operations Management. Each has unique goals and practices. Understanding these can help your business run smoothly. Let’s dive into their specifics.
Project Management Overview
Project Management focuses on completing specific tasks. These tasks have a clear start and end. They often aim to create a unique product or service. Project managers oversee planning, execution, and closing. They ensure projects meet deadlines and stay within budget.
- Scope: Defines the project’s boundaries and deliverables.
- Time: Manages the project timeline and milestones.
- Cost: Controls the project budget.
- Quality: Ensures the final output meets standards.
- Stakeholder Management: Engages and manages project stakeholders.
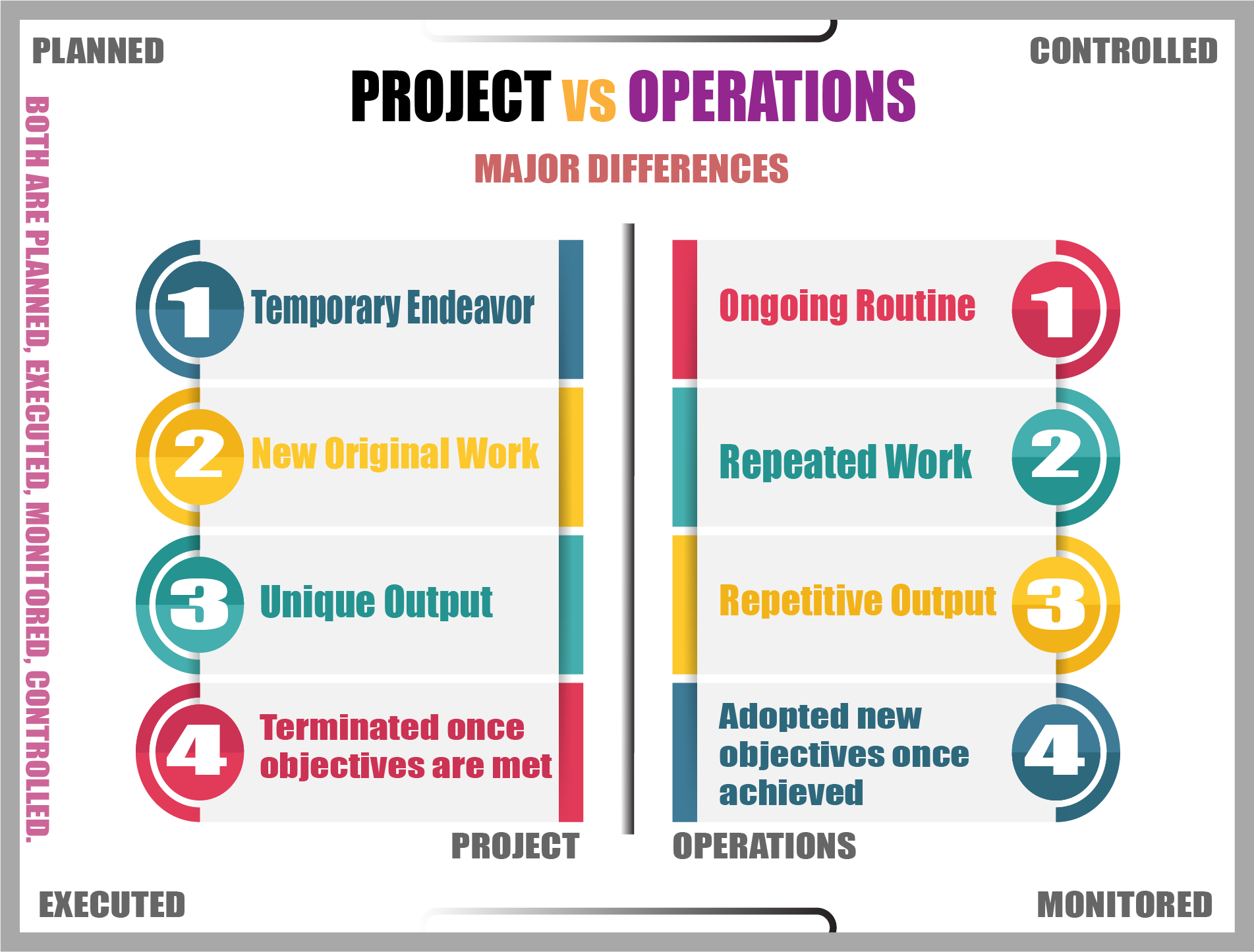
Project management is dynamic and temporary. Each project is unique and requires a tailored approach.
Operations Management Overview
Operations Management deals with ongoing activities. It ensures daily operations run smoothly. Operations managers focus on efficiency and consistency. Their goal is to optimize processes and improve productivity.
| Aspect | Project Management | Operations Management |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Temporary | Ongoing |
| Focus | Specific Goals | Continuous Improvement |
| Scope | Defined and Limited | Broad and Continuous |
| Output | Unique Deliverables | Standardized Products/Services |
Operations management is stable and repetitive. It ensures the consistency of products or services.
Both disciplines are crucial for success. Knowing their differences helps in assigning the right tasks to the right managers.
Core Objectives
The core objectives of project management and operations management are fundamentally different. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses aiming to achieve both short-term and long-term goals. Let’s dive into the distinct goals of each discipline.
Goals Of Project Management
Project management focuses on achieving specific, temporary goals. Here are the primary objectives:
- Delivering unique outputs: Projects are designed to produce specific deliverables.
- Meeting deadlines: Projects have fixed start and end dates.
- Managing resources: Effective allocation of resources is key.
- Ensuring quality: High standards must be maintained throughout the project.
- Risk management: Identifying and mitigating risks is crucial.
Goals Of Operations Management
Operations management aims to maintain and improve ongoing activities. Here are its main objectives:
- Efficiency: Streamlining processes to maximize productivity.
- Consistency: Ensuring consistent output quality.
- Customer satisfaction: Meeting customer needs effectively.
- Cost control: Reducing costs while maintaining quality.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly improving processes and systems.
To summarize, project management is about achieving specific, temporary goals. Operations management focuses on ongoing activities. Both are vital for business success.
Key Roles And Responsibilities
Understanding the key roles and responsibilities of project management and operations management helps define their distinct functions. Though both roles are crucial, they focus on different aspects of an organization. Below, we delve into the specific duties of each role.
Project Manager Duties
A project manager oversees temporary projects. Their primary goal is to ensure the project is completed on time, within scope, and on budget. Key responsibilities include:
- Defining project scope and objectives
- Developing detailed project plans
- Allocating resources
- Managing project budgets
- Leading project teams
- Monitoring project progress
- Communicating with stakeholders
- Ensuring project deliverables meet quality standards
The project manager must also manage risks and handle any issues that arise during the project lifecycle. They play a crucial role in ensuring project success through effective planning and execution.
Operations Manager Duties
An operations manager handles the ongoing operations of an organization. Their focus is on maintaining and improving efficiency, productivity, and quality. Key responsibilities include:
- Managing day-to-day operations
- Overseeing production processes
- Developing and implementing operational policies
- Monitoring performance metrics
- Ensuring compliance with regulations
- Optimizing resource use
- Managing operational budgets
- Supervising staff
The operations manager must continuously look for ways to improve processes and systems. They focus on long-term operational success and sustainability.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Scope And Focus
Understanding the scope and focus of project management and operations management is crucial. These two disciplines play distinct roles within an organization. Their objectives and approaches differ significantly. Let’s dive into their unique characteristics through the lens of scope and focus.
Project Scope
Project management revolves around specific tasks. These tasks have a start and end date. The project scope includes defining objectives, deliverables, tasks, and deadlines. Projects are temporary and unique. They aim to achieve a particular outcome or create a unique product or service.
In project management, scope definition is vital. It involves identifying all the work needed to complete the project. The scope statement outlines the project’s boundaries. It helps in managing expectations and avoiding scope creep. Project managers use scope management techniques to ensure successful delivery.
Common elements in project scope include:
- Project objectives
- Deliverables
- Tasks and activities
- Milestones
- Deadlines
Operational Scope
Operations management focuses on ongoing activities. These activities are repetitive and continuous. The operational scope includes managing processes, systems, and resources. Operations aim to maintain and improve efficiency and productivity.
Operational scope covers day-to-day functions of an organization. It ensures that business operations run smoothly. Operations managers oversee various functions such as production, quality control, and supply chain management. They focus on optimizing processes and reducing costs.
Key elements in operational scope include:
- Process management
- Resource allocation
- Quality control
- Supply chain management
- Continuous improvement
In summary, project management deals with unique, time-bound tasks. Operations management handles ongoing, repetitive activities. Both are essential for an organization’s success. Understanding their distinct scopes helps in better resource allocation and management.
Timeframes And Durations
Understanding the differences between Project Management and Operations Management is crucial for any business. One of the key distinctions lies in their timeframes and durations. Projects have a set timeline, while operations are ongoing.
Project Timelines
Projects are temporary. They have a clear start and end date. The timeline depends on the project’s scope and goals. Typically, a project timeline includes:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Closure
Each phase has specific tasks and milestones. The goal is to complete the project on time and within budget. This requires careful planning and scheduling.
A Gantt Chart is often used to track project timelines. It visually represents the schedule. It shows start and end dates for each task.
Ongoing Operations
Operations are continuous and repetitive. They do not have a set end date. The focus is on maintaining and improving daily activities.
Operations include tasks such as:
- Production
- Maintenance
- Customer Service
- Quality Control
These tasks are performed regularly. The goal is to ensure smooth and efficient processes. This requires consistent monitoring and management.
In operations management, timeframes are cyclical. Managers look at daily, weekly, and monthly cycles. They aim to optimize performance and reduce downtime.
| Aspect | Project Management | Operations Management |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Temporary | Ongoing |
| Focus | Specific Goals | Continuous Improvement |
| Tools | Gantt Chart | Cycle Analysis |
Tools And Techniques
Understanding the differences between project management and operations management is crucial for businesses. Each discipline uses different tools and techniques to achieve their goals. In this section, we will explore the tools and techniques used in both project management and operations management.
Project Management Tools
Project management focuses on completing specific tasks within a defined timeline. Here are some essential tools used in project management:
- Gantt Charts: Visual timelines that help track project progress.
- Critical Path Method (CPM): Identifies the longest sequence of tasks.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Breaks down a project into smaller components.
- Project Management Software: Tools like Asana and Trello help manage tasks and deadlines.
- Risk Management Tools: Identifies and mitigates potential risks.
Operations Management Tools
Operations management focuses on ongoing processes to maintain and improve efficiency. Here are some key tools used in operations management:
- Six Sigma: A methodology to reduce defects and improve quality.
- Lean Manufacturing: Focuses on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Ensures all employees are committed to improving quality.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Integrates all facets of an operation, including planning, purchasing, inventory, and sales.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Metrics used to evaluate the success of an activity.
Both project management and operations management have unique tools and techniques. These tools help achieve specific goals, whether it’s completing a project or improving ongoing processes.
Challenges And Solutions
Understanding the differences between Project Management and Operations Management can be complex. Both fields face unique challenges. Knowing these challenges and solutions can help improve efficiency and productivity in your organization.
Project Management Challenges
Project management involves specific tasks with deadlines. These challenges often include:
- Time Management: Meeting deadlines can be tough. Delays can occur due to unforeseen issues.
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring the right resources are available at the right time is crucial.
- Scope Creep: Uncontrolled changes can derail the project. It can lead to missed deadlines and budget overruns.
- Communication: Effective communication among team members is vital. Miscommunication can cause errors and delays.
Solutions to these challenges include:
- Time Management: Use project management tools to track progress. Set realistic deadlines and milestones.
- Resource Allocation: Plan resource needs in advance. Use resource management software to allocate resources efficiently.
- Scope Creep: Define project scope clearly at the start. Manage change requests carefully.
- Communication: Hold regular meetings. Use collaboration tools to keep everyone on the same page.
Operations Management Challenges
Operations management focuses on ongoing activities. Common challenges include:
- Efficiency: Maintaining high efficiency is critical. Inefficiencies can lead to increased costs and lower productivity.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality is a continuous challenge. Poor quality can harm reputation and customer satisfaction.
- Inventory Management: Balancing inventory levels is crucial. Too much or too little inventory can be costly.
- Process Optimization: Continuously improving processes is essential. Stagnation can lead to inefficiencies and higher costs.
Solutions to these challenges include:
- Efficiency: Implement lean management techniques. Regularly review and improve processes.
- Quality Control: Use quality management systems. Conduct regular audits and training sessions.
- Inventory Management: Use inventory management software. Maintain optimal stock levels through just-in-time (JIT) practices.
- Process Optimization: Continuously seek feedback and improvements. Use data analytics to identify areas for improvement.
Interrelationship And Collaboration
Understanding the interrelationship and collaboration between project management and operations management is crucial for business success. Both areas have distinct roles but often intersect to achieve organizational goals. This section delves into how these functions work together and the benefits of their collaboration.
How They Work Together
Project management focuses on achieving specific goals within a set timeframe. On the other hand, operations management deals with ongoing processes that sustain the business. Despite their differences, both must align to ensure seamless workflow.
Here’s how they collaborate:
- Resource Allocation: Project managers and operations managers work together to allocate resources efficiently.
- Process Improvement: Operations managers often provide insights that help project managers improve project processes.
- Risk Management: Both roles assess risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Benefits Of Collaboration
Collaborating between project management and operations management offers several benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Efficiency | Collaboration ensures that resources are used optimally, reducing waste and increasing efficiency. |
| Enhanced Communication | Regular interaction between teams leads to better communication and fewer misunderstandings. |
| Better Risk Management | Both teams can identify potential risks early and develop effective mitigation strategies. |
| Higher Quality Outcomes | Combining project and operational insights often results in higher-quality deliverables. |
Effective collaboration between project management and operations management can drive an organization toward its strategic goals more effectively.
Credit: www.iliyanastareva.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Project Management?
Project management involves planning, executing, and closing projects. It focuses on achieving specific goals within a defined timeline and budget.
What Is Operations Management?
Operations management focuses on ongoing business operations. It ensures that daily activities run smoothly and efficiently to meet organizational goals.
How Do Project Management And Operations Management Differ?
Project management deals with temporary projects with specific goals. Operations management handles continuous processes that support the company’s long-term objectives.
Can One Person Handle Both Project And Operations Management?
While possible, it’s challenging. Each requires different skills and focus. Larger organizations often have separate managers for each role.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between project management and operations management is crucial. Project management focuses on temporary, unique tasks. Operations management deals with ongoing activities. Both roles require different skills and approaches. Knowing their distinctions helps in better decision-making. It also aids in efficient resource allocation.
Clear roles lead to smoother workflows. They ensure goals are met effectively. This knowledge improves organizational success. Keep learning and applying these principles. Your projects and operations will thrive.






